Are your emails landing in spam folders instead of your recipients’ inboxes? If you’re struggling with email deliverability issues and want to protect your domain from email spoofing and phishing attacks, implementing proper email authentication protocols is crucial for your success.

In 2025, major email providers like Gmail, Yahoo, and Microsoft have made SPF, DKIM, and DMARC implementation mandatory for high-volume senders.
This comprehensive guide will show you exactly how to implement these email security protocols to boost your sender reputation, improve email deliverability, and protect your business email from malicious attacks.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Email Authentication and Why It Matters
Email authentication is the process of verifying that emails sent from your domain are legitimate and haven’t been tampered with during transmission. Think of it as a digital ID card that proves you are who you claim to be when sending emails.
The Current Email Authentication Crisis

Recent statistics reveal alarming trends:
- 93% of phishing emails contain encryption ransomware
- 3.4 billion phishing emails are sent daily
- Companies lose approximately $1.6 billion annually due to phishing attacks
- 70% of global emails are considered malicious
2025 Email Authentication Requirements
Starting February 2024, and continuing into 2025, major email providers have implemented strict requirements:
Google & Yahoo Requirements:
- Required DMARC protocol deployment for high-volume email senders (5,000+ messages per day)
- Mandatory SPF and DKIM configuration for sender domain verification
- Spam complaint rates must stay below 0.30%
Microsoft’s New Policy (May 5, 2025):
- SPF, DKIM, and DMARC authentication required for high-volume senders
- Messages failing compliance standards will be blocked and return error status 550 5.7.15
- Impacts all messages delivered to Outlook.com, Hotmail.com, and Live.com addresses
Understanding the Email Authentication Trinity: SPF, DKIM, and DMARC
1. SPF (Sender Policy Framework) – Your Email Bouncer
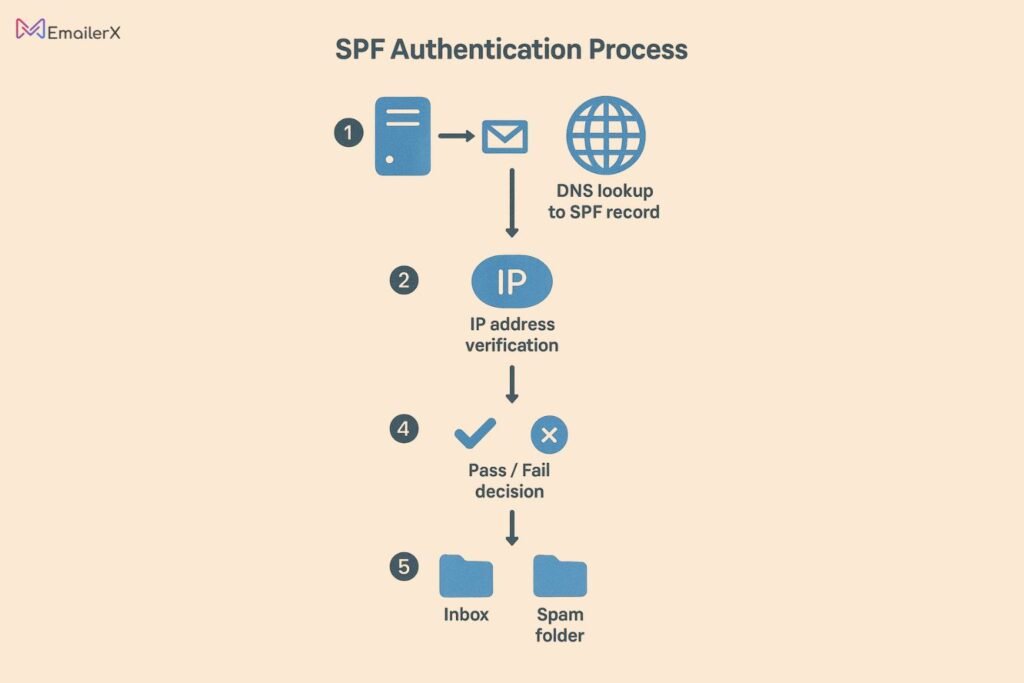
SPF records act like a guest list for your domain, specifying which IP addresses are authorized to send emails on your behalf.
How SPF Works:
- You create a DNS TXT entry that specifies which servers are permitted to send emails on your domain’s behalf
- Recipient mail servers verify whether the sender’s IP address corresponds with your published SPF authentication record
- When the IP address aligns with your SPF record, the message successfully clears SPF verification
- When verification fails, the message risks being flagged as unwanted mail or completely blocked by the receiving server
SPF Record Example:
v=spf1 include:_spf.google.com include:mailgun.org ~all
Common SPF Issues:
- SPF record exceeds 10 DNS lookup limit – This causes authentication failures
- Multiple SPF records for the same domain
- Incorrect syntax in DNS records
2. DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) – Your Digital Signature
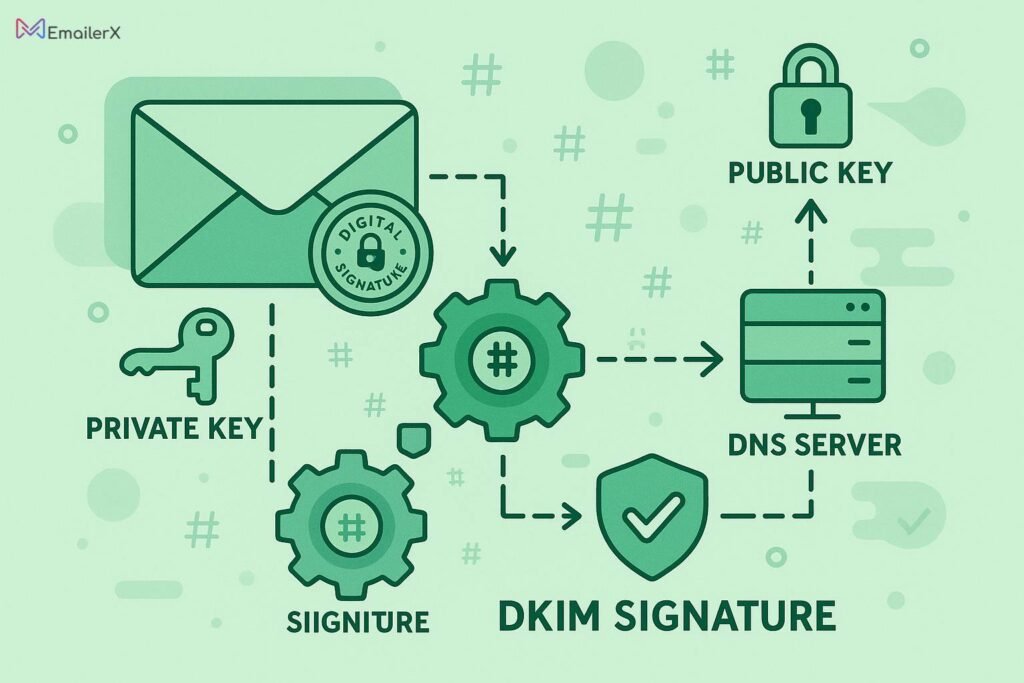
DKIM verification incorporates a cryptographic signature into your messages, guaranteeing their content remains unchanged throughout the delivery process.
DKIM Process:
- Your email server signs outgoing emails with a private key
- Your DNS settings include a published DKIM entry that houses the public encryption key for verification purposes
- Recipient mail servers utilize the published public key to authenticate the message’s digital signature
- If verification succeeds, DKIM authentication passes
Benefits of DKIM Setup:
- Protects against email header authentication tampering
- Works even when emails are forwarded
- Improves email marketing deliverability
- Essential for cold email authentication setup
DKIM Key Rotation Best Practices:
- Rotate keys annually for enhanced security
- Use multiple selectors for redundancy
- Store private keys securely (AWS Secrets Manager, HashiCorp Vault)
3. DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) – Your Policy Enforcer
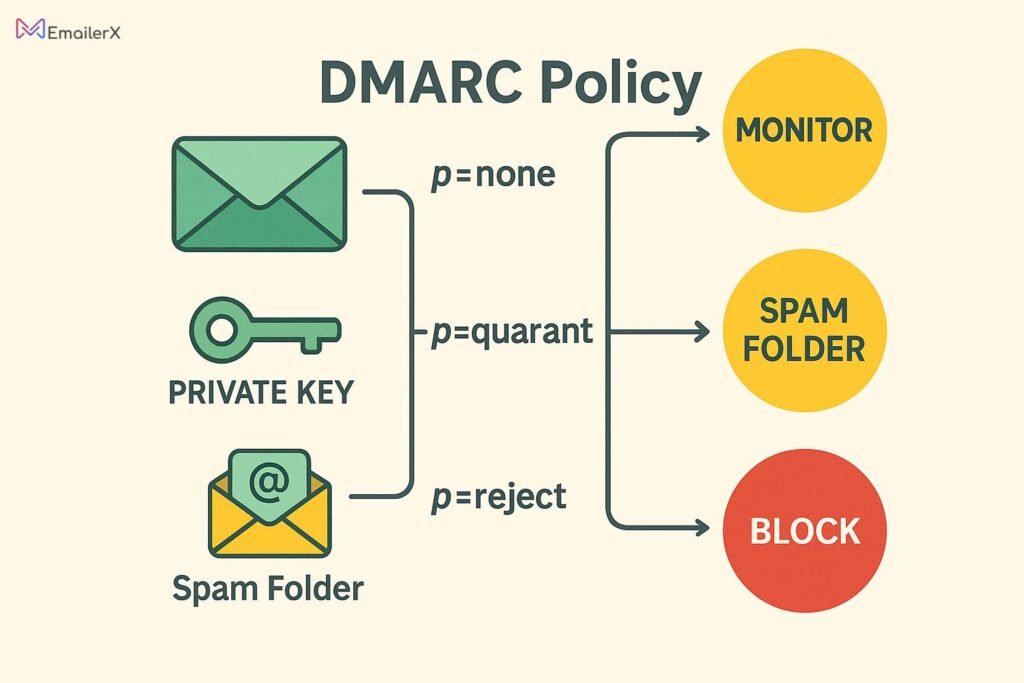
DMARC implementation combines SPF and DKIM results to make authentication decisions and provides detailed reporting.
DMARC Policy Options:
- p=none – Monitor mode (no action taken)
- p=quarantine – Send failing emails to spam folder
- p=reject – Reject failing emails completely
DMARC Alignment: Strict vs Relaxed:
- Strict alignment – Domains must match exactly
- Relaxed alignment – Organizational domains must match (subdomains allowed)
Step-by-Step Guide: Implementing SPF, DKIM, and DMARC for Email Authentication
Phase 1: SPF Record Setup
1. Audit Your Email Sources
- List all services sending emails from your domain
- Include: your mail server, ESP (MailChimp, SendGrid), CRM systems
- Document IP addresses for each service
2. Create Your SPF Record
v=spf1 ip4:192.168.1.100 include:_spf.google.com include:sendgrid.net ~all
3. Publish SPF Record
- Log into your DNS provider (GoDaddy, Cloudflare, Namecheap)
- Add a TXT record for your domain
- Set the value to your SPF record
- Wait for DNS propagation (up to 48 hours)
Pro Tip: Use tools like MXToolbox SPF Checker to validate your record and avoid the 10 DNS lookup limit.
Phase 2: DKIM Setup for Different Platforms
Google Workspace DKIM Configuration
- Access Google Admin Console
- Access Apps → Google Workspace → Gmail → Email Authentication settings
- Generate DKIM key pair
- Insert the supplied CNAME entry into your domain’s DNS configuration
MailChimp DKIM Authentication
- Go to Account → Settings → Domains
- Add your domain and verify ownership
- Copy the provided DKIM records
- Add CNAME records to your DNS settings
SendGrid DKIM Implementation
- Access Sender Authentication settings
- Select “Authenticate Your Domain”
- Choose your DNS host
- Insert the created CNAME entries into your domain’s DNS settings
Phase 3: DMARC Implementation Strategy
Step 1: Start with Monitoring
v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:dmarc@yourdomain.com; ruf=mailto:dmarc@yourdomain.com
Step 2: Gradual Policy Enforcement
- Monitor for 2-4 weeks with p=none
- Analyze DMARC reports for authentication failures
- Fix any legitimate senders failing authentication
- Gradually move to p=quarantine, then p=reject
Step 3: Advanced DMARC Configuration
v=DMARC1; p=reject; rua=mailto:dmarc@yourdomain.com; ruf=mailto:dmarc@yourdomain.com; pct=100; adkim=r; aspf=r
Platform-Specific Email Authentication Setup
Cold Email Authentication Setup
For high-volume outreach and cold email campaigns:
Essential Requirements:
- Implement domain warming alongside authentication
- Use dedicated subdomains for cold outreach
- Monitor sender reputation closely
- Set up proper SMTP authentication protocols
Recommended Tools:
- Instantly.ai – Built-in domain warming with authentication
- Lemlist – Advanced deliverability features
- Woodpecker – Comprehensive authentication setup
CRM Email Authentication Setup
For sales email deliverability optimization:
HubSpot Configuration:
- Navigate to Settings → Domains & URLs
- Connect your email sending domain
- Complete DNS verification process
- Set up tracking domains for better deliverability
Salesforce Email Authentication:
- Access Setup → Email Administration
- Configure Deliverability settings
- Add your domain’s SPF and DKIM records
- Enable DMARC policy monitoring
Email Marketing Platform Authentication
Klaviyo Email Authentication:
- Go to Account → Settings → Sending
- Add and verify your sending domain
- Configure SPF and DKIM records
- Set up dedicated IP (for high-volume senders)
ActiveCampaign Setup:
- Go to Settings → Advanced → Domain Verification
- Choose “Configure Domain” for automatic setup
- Follow DNS configuration instructions
- Verify authentication status
Troubleshooting Common Email Authentication Issues
Why Emails Are Still Going to Spam
Even with proper SPF, DKIM, and DMARC implementation, emails might still face deliverability issues:
Content-Related Factors:
- Spammy subject lines
- Poor sender reputation
- High complaint rates
- Blacklisted IP addresses
Technical Issues:
- Envelope from vs header from misalignment
- DMARC alignment failures
- Incorrect DNS record configuration
- DKIM signature validation errors
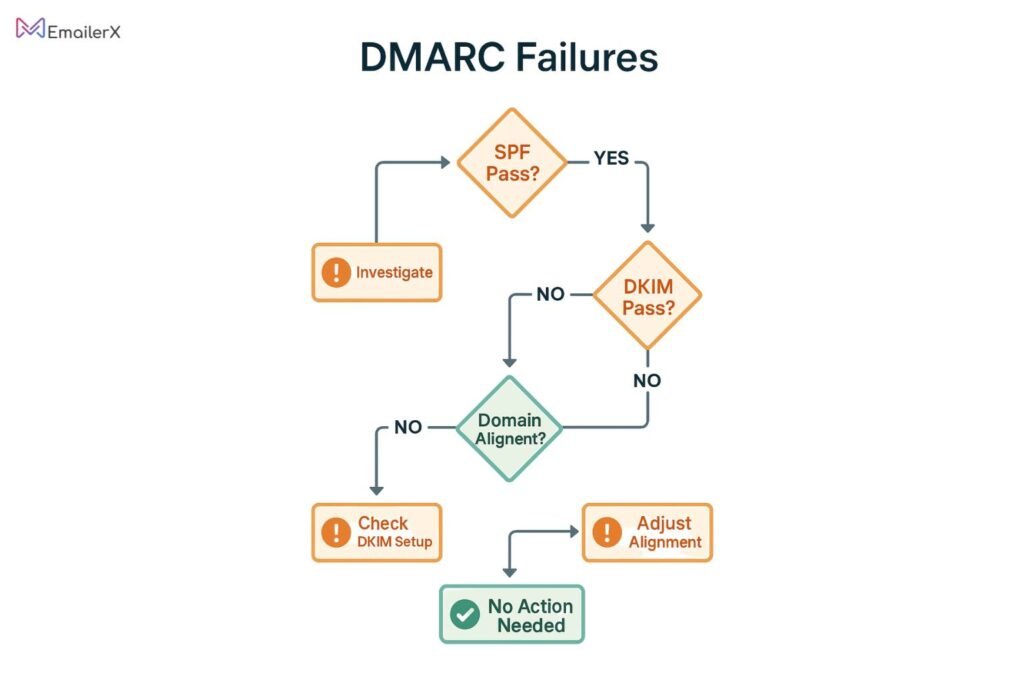
DMARC Failing When SPF and DKIM Pass
This common issue occurs due to domain alignment problems:
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Confirm that your “From” header domain aligns with your configured SPF/DKIM domain settings
- Check DMARC alignment settings (strict vs relaxed)
- Ensure proper subdomain configuration
- Review email routing through third-party services
SPF Record Exceeds 10 DNS Lookup Limit
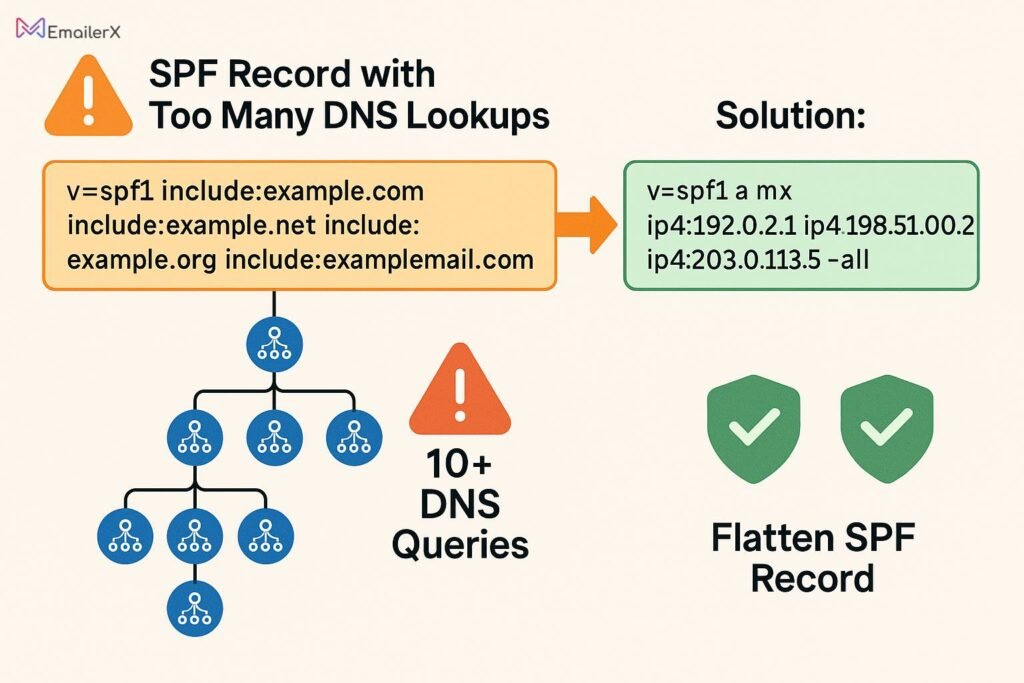
Solutions:
- SPF flattening – Convert includes to IP addresses
- Use dedicated subdomains for different services
- Implement SPF record optimization tools
- Consider managed SPF services
Essential Email Authentication Tools and Resources
Free Authentication Checkers
DMARC Analyzers:
- DMARCLY Free Tools – Comprehensive SPF/DKIM/DMARC checkers
- MXToolbox DMARC Check – Professional DNS diagnostics
- EasyDMARC Lookup Tool – Free 14-day trial with advanced features
SPF Validators:
- EasyDMARC SPF Validation Tool – Verifies SPF record format and DNS query resolution
- DMARCLY SPF Tool – Includes flattening capabilities
Premium Email Authentication Platforms
Enterprise Solutions:
- DMARCLY – Comprehensive monitoring and automation
- EasyDMARC – Full-service authentication platform
- Valimail – Enterprise-grade DMARC enforcement
- Proofpoint – Advanced threat protection with authentication
Email Deliverability Audit Tools
Recommended Services:
- MailGenius – Complete deliverability analysis
- GlockApps – Inbox placement testing
- 250ok – Email intelligence platform
Email Authentication Best Practices for 2025
Domain Reputation Management
Key Strategies:
- Use dedicated IPs for high-volume sending
- Implement proper domain warming procedures
- Monitor blacklist status regularly
- Maintain low complaint rates (<0.1%)
Multi-Domain Email Authentication
For agencies managing multiple clients:
- Set up subdomain strategies for different campaigns
- Implement centralized DNS management
- Use automated monitoring tools
- Provide client education on authentication importance
Advanced Security Measures
Additional Protections:
- Implement BIMI (Brand Indicators for Message Identification)
- Set up MTA-STS for encrypted email delivery
- Use ARC (Authenticated Received Chain) for forwarded emails
- Enable TLS reporting for security insights
Email Authentication ROI and Business Impact
Measurable Benefits
Deliverability Improvements:
- 10-15% increase in inbox placement rates
- 25-40% reduction in spam folder placement
- 20-30% improvement in email open rates
- 15-25% boost in click-through rates
Security Benefits:
- 99% reduction in successful domain spoofing
- 80% decrease in phishing attempts using your domain
- Enhanced brand protection and customer trust
- Compliance with industry regulations
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Implementation Costs:
- Time investment: 4-8 hours for basic setup
- Tool costs: $50-500/month for enterprise solutions
- Professional services: $1,000-5,000 for complex implementations
Return on Investment:
- Increased revenue from better email deliverability
- Reduced security incident costs
- Improved customer trust and brand reputation
- Compliance with email provider requirements
Email Deliverability Audit Checklist
Pre-Implementation Assessment
Domain Health Check:
- Verify domain age (minimum 30 days)
- Check blacklist status
- Analyze current authentication status
- Review sending reputation
Technical Requirements:
- DNS access and management capabilities
- List of all email sending services
- IP address inventory
- Current email volume analysis
Post-Implementation Verification
Authentication Validation:
- SPF record syntax verification
- DKIM signature validation
- DMARC policy testing
- DNS propagation confirmation
Performance Monitoring:
- DMARC report analysis
- Deliverability rate tracking
- Complaint rate monitoring
- Authentication failure investigation
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if I don’t implement email authentication?
Without proper SPF, DKIM, and DMARC setup, your emails face several risks:
Higher spam folder placement rates
Increased rejection by major email providers
Vulnerability to domain spoofing attacks
Poor sender reputation
Potential blacklisting by ISPs
How long does email authentication implementation take?
Timeline varies by complexity:
Basic setup: 2-4 hours for simple configurations
Complete implementation: 1-2 weeks including testing and monitoring
Enterprise deployment: 2-4 weeks with multiple domains and services
DNS propagation: 24-48 hours for changes to take effect
Can I implement DMARC without SPF and DKIM?
While technically possible to publish a DMARC record without SPF and DKIM, it’s not recommended. DMARC relies on SPF and/or DKIM results to function properly. For effective email authentication:
Implement SPF first
Add DKIM authentication
Deploy DMARC with monitoring mode
Gradually enforce stricter policies
What’s the difference between DMARC quarantine vs reject?
DMARC Policy Comparison:
p=quarantine:
Failing emails go to spam/junk folder
Recipients can still access messages
Safer during initial implementation
Allows for gradual policy enforcement
p=reject:
Failing emails are completely blocked
Recipients never see unauthorized messages
Maximum security protection
Requires careful preparation to avoid blocking legitimate emails
How do I fix “SPF record exceeds 10 DNS lookup limit”?
Solutions for SPF Lookup Limit:
SPF Flattening – Convert includes to IP addresses
Subdomain Strategy – Use separate domains for different services
Managed SPF Services – Use third-party SPF management tools
Record Optimization – Remove unnecessary includes and mechanisms
Is email authentication required for cold email campaigns?
Yes, cold email authentication is essential for:
Avoiding spam filters
Maintaining sender reputation
Complying with ESP requirements
Protecting domain from spoofing
Improving overall deliverability rates